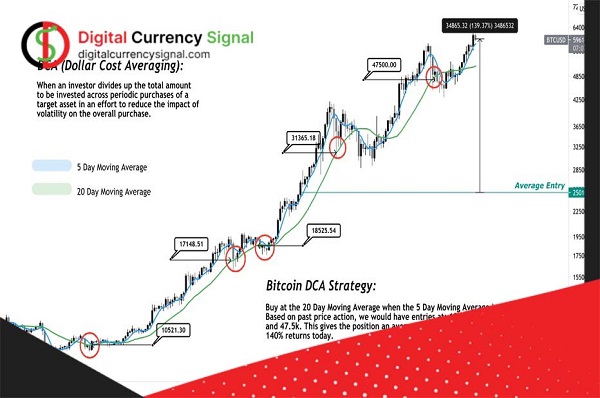
Blockchain technology is an expanding and evolving technology that needs to be updated and upgraded. While the blockchain itself cannot be changed, the tokens or coins offered on the blockchain platform can be changed. This is where a concept called a fork comes in. Updating or creating a new blockchain is called a fork. Forks are necessary to make changes to the blockchain, such as new rules or bug fixes. There are two main types of programming forks, called hard forks and soft forks.
A hard fork is a modification of a coin protocol where previously invalid blocks and transactions are processed. Therefore, all users should apply it. Hard forks are not backward compatible. A hard fork sometimes causes the conversion of two currencies, for example, Bitcoin Cash is a hard fork of Bitcoin, or Ethereum Classic is a hard fork of Ethereum, and this causes the appearance of two completely separate currencies, and those who want can use the former Continue or switch to a new hard fork.
What is a fork?
To understand what a hard fork is, we must first define the term “fork”. Fork is a specialized term in computer and software science that refers to the act of creating a new program by changing the protocol of open-source software. When software is forked, its source code is copied by other developers and then various changes are made to that code to get new output. The concept of a fork in the blockchain is also similar to this issue, but there are also differences.
In a blockchain, miners or network validators must agree with each other to reach a consensus on the final state of the distributed ledger. For this to happen, a network-wide protocol was created that explains the working state of the blockchain to miners. Among the important aspects of the protocol, we can mention the size of the blocks, the total amount of currencies in the blockchain, the hash functions used, and the structure of the data layout in the blockchain.

Now, if there are problems in the protocol or if network users want to improve its performance by changing the protocol variables, they need to fork the blockchain. A fork in the blockchain means creating a new block along with the previous block using a new protocol. Of course, there are different types of forks in the blockchain, and the above definition mainly concerns the types of “soft fork” and “preprogrammed hard fork”.
What is a hard fork?
Forks on the blockchain are divided into two categories, “soft fork” and “hard fork”, depending on whether changes in the protocol are backward compatible or not. A major fork refers to changes that are not compatible with the previous protocol (unrelated) so after the fork, only users who update their software will be able to verify that blocks and miners have also developed new software.
The hard fork is a fundamental change to the blockchain, so blocks formerly known as valid blocks are no longer valid, and blocks that were previously invalid can be considered valid with the new protocol. Note that in a hard fork, we have nothing to do with the previous blocks of the blockchain, and no changes are made to them. Next, to better understand a hard fork, we will use the example of the Bitcoin protocol to take a look at the events that can occur as a result of a hard fork together.
Possible results of a hard fork
After each hard fork, we will see two networks with different events happening to them. A hard fork can be considered a milestone in any blockchain with significant consequences. Each hard fork or soft fork results in one of the following events:
- One of the blockchains will dominate, as a result, the other blockchain will not be as popular and the coin created will have a lower value. We use the word “maybe” here because in a soft fork like Segwit, we only have two programs, and no coins are created.
- Both blockchains are welcome, as a result, both continue to operate independently and with roughly the same user base. Segwit is a good example of this phenomenon.
- Both blockchains are accepted, but one is getting more popular. An example of this hard fork is Bitcoin Cash, which continues to be effective along with Bitcoin but is not as popular. Ethereum is an example of this type of hard fork, descended from Ethereum Classic.
What effect does the fork have on the price?
Forks can have a huge impact on cryptocurrencies. Often a hard fork can have a tangible impact on the price of cryptocurrencies. Because a fork is a process that updates the network and changes the way the digital currency blockchain works. This change is similar to an upgrade that replaces an old version with a new version on a hard fork. Merchants can replace the latest version with the new version. When this happens, the coin loses its value.
For example, when the Bitcoin network forks, a small amount of value in the network is split into a forked chain. When Bitcoin Cash was charged from the Bitcoin network, the price of Bitcoin went from $2,800 to $2,700. This fork effect means that assets can decrease in value. Despite the loss of the primary currency, the increase in the value of the secondary currency makes up for it. Besides the blockchain and cryptocurrency prices, forks can also affect other things like the metaverse.
Conclusion
While there has always been a lot of criticism of forks throughout the history of cryptocurrency, we have to admit that forks are generally beneficial to the cryptocurrency community. The developments in the field of digital currency are happening step by step and currently, the only way to use these developments is through forks. Also, it is this fork that brings the voices of all members of this community and their criticisms and suggestions to the ears of the developers.
Don’t forget that the project’s developers and founders are only pieces of this puzzle. To improve the blockchain, Various groups, from network nodes to ordinary users and wallet servers, must support the proposed changes and agree on their details.