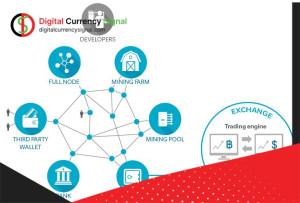
Blockchain is a decentralized network with records stored in blocks. Each block is associated with a time stamp and can be stored on any computer that processes transactions on the blockchain. In fact Blockchain is managed and controlled by a network of computers called nodes that distribute blocks in a database. For this reason, in this part of the discussion on digital currency education, we want to provide you with explanations about Full Note, examine the advantages and disadvantages of Full Note, and examine the effectiveness of Full Node.
What is a full node?
A full node in a blockchain refers to the nodes where all network information is recorded. These nodes receive and store all transactions and blocks created. In addition to this responsibility, the full node is responsible for the synchronization and distribution of data and the validation of new blocks. Among other tasks of the full node in the blockchain network, we can mention the creation of a reliable and transparent database.
By performing these tasks, the full node ensures the security of the network and confirms the authenticity of the data; Consequently, the higher the number of nodes in a network, the higher its reliability and security. Complete nodes follow the rules of the network voluntarily, and if the number increases, the strength of the network increases.
How is the full node performance?
If the blockchain is planned for the future, all the nodes will analyze the existing proposals and decide to accept them or reject them. In order for each proposal to be accepted, it is necessary that more than 51% of the total nodes agree, and if this does not happen, the proposal will not be implemented in the network – the blockchain. Sometimes this can lead to a hard fork. When a blockchain network’s community cannot agree on a particular change, they go their separate ways and create two separate chains. The most famous example of a hard fork is the Bitcoin Cash (BCH) fork of the Bitcoin crypto.

What are the types of full nodes?
Full nodes are divided into two subgroups:
Pruned full node
The main feature of a fully managed network node is the memory limit it imposes. Pruning starts when a node downloads a block completely and starts removing all metadata from the oldest recorded blocks, keeping only the latest entries. This node’s performance prioritizes security over storage.
Archival full node
A full-archive network node stores all ledgers and records all transactions up to the block of origin. These types of muscles are common and are classified into four groups: (Authority nodes)، (Mining nodes)، (Master nodes) ،(Staking nodes).
Advantages of running a full node
- One advantage of running a full node is that you don’t need to trust users or intermediaries. In other words, by implementing a full node in the Bitcoin network, you don’t have to rely on others for the health and security of the network.
- High security and privacy protection is another benefit of running a full node. To use the peer system, you must be a peer yourself. Otherwise, your transaction will always be processed through a broker.
- When the blockchain hits a hard fork, Litenodes automatically follows the chain with the biggest accumulation problem.
Disadvantages of full node implementation
- One drawback of full node processing is disk space and RAM partitioning. You need to download the entire blockchain network for network initial compatibility, and this setup requires a lot of disk space.
- Getting full sleep is hard work. The minimum recommended bandwidth for the Bitcoin Core network is approximately 5 GB upload and 500 MB download per day.
- Implementing a full node on the Bitcoin network requires a lot of basic equipment, and if possible, you should do the initial implementation with a powerful tool. Also, the cost of electricity consumption of complete nodes can be very high.
Full Node Bitcoin
Bitcoin full nodes store the entire blockchain data. This means that it contains information about all blocks and the full history of transactions that took place in these blocks. By default, a Bitcoin full node owns the entire blockchain database, which means that there must be at least one full node in the entire network. In fact, there are several full nodes in many cryptocurrency networks. As we mentioned earlier, in order for a node to operate on a block, it is not necessary to store the entire blockchain. But access to the full record allows full Bitcoin nodes to perform additional operations.
What are the advantages of Bitcoin full node?
Converting a node to a full node is expensive and does not benefit volunteer nodes in any way. Many people volunteer on the network and play the role of a full Bitcoin node. This requires the use of additional processing resources and higher costs. It should be noted that a large number of volunteers are needed to fully develop the Bitcoin Node network, and a limited number is not working. Instead, enhance network security; secure wallets for holding bitcoins; Benefits such as selling data to merchants are listed for the full button.
Last word
The role of a node in a blockchain network is similar to the role of a server in the Internet space. The main benefit of a full node configuration is maintaining full network security. On the other hand, this article is considered very useful and important for those for whom secure transaction confirmation is important and communication is safe from attacks. Despite all the pros and cons, you need to weigh up whether a full network setup can make or break you, based on your business and how much you use your network.